How to Decide Which Probability Distribution to Use
Probability can only be calculated when the event whose. A distribution is called Poisson distribution when the following assumptions are valid.
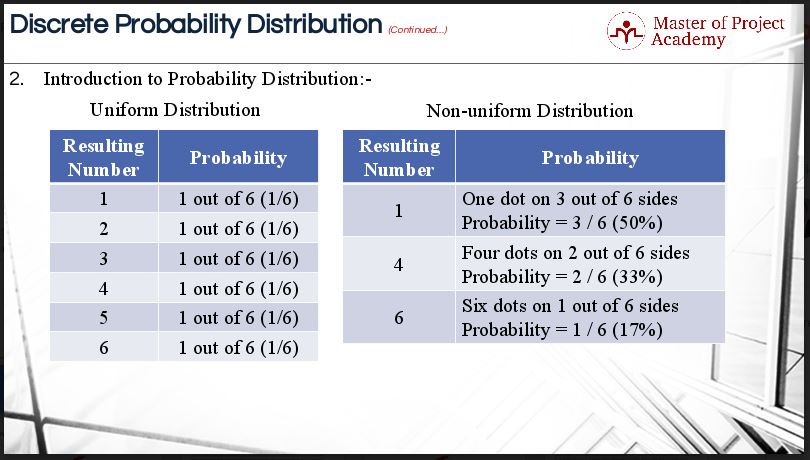
Understanding Discrete Probability Distribution
Thinking critically and logically will help you to decide on things wisely.

. The probability of success over a short interval must equal the probability of success over a longer interval. Steps to creating a frequency distribution illustrated with 4 examples labelled A B C and D. The probability of success in an interval approaches.
It is created with roleplaying games in mind. It is a must that you should be wise when making decisions. A bell curve a graph of your data can help you decide whether or not your data is normal.
Choose an event with mutually exclusive outcomes. We denote this by X. In order to use a z-table you need to split your z-value up into decimal places eg.
Even if we have complete mechanistic knowledge of our process the concepts from probability and statistics are useful to summarize and communicate information about past behaviour and the expected future behaviour. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1 where roughly speaking 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty. 95 of a Probability Distributions Decision-making is an important skill that each individual should acquire.
There are many problem domains where describing or estimating the probability distribution is relatively straightforward but calculating a desired quantity is intractable. Any successful event should not influence the outcome of another successful event. 44 Normal random variables.
Monte Carlo methods are a class of techniques for randomly sampling a probability distribution. Steps for finding the area in a z-table. It is often referred to as the bell curve because its shape resembles a bell.
This is where p i is the probability of getting each value and. A random variable X is said to have a chi-square χ 2 distribution with n degrees of freedom if and only if X is a gamma random variable with parameters α n2 and β 2. For a discrete probability distribution like this variance can be calculated using the equation below.
For example if you are asked to find the area in a one tailed distribution with a z-value of 021 split this into tenths 02 and hundredths 001. Roll of a die Probability mass function pmf Cumulative distribution function CDF Cumulative distribution function. The importance of the normal distribution stems from the Central Limit Theorem which implies that many random variables have normal distributionsA little more accurately the Central Limit Theorem says.
Making a histogram of your data can help you decide whether or not a set of data is normal but there is a more specialized type of plot you can create called a normal probability plot. Poisson Distribution is a type of distribution which is used to calculate the frequency of events which are going to occur at any fixed time but the events are independent in excel 2007 or earlier we had an inbuilt function to calculate the Poisson distribution for versions above 2007 the function is replaced by PoissonDIst function. Times New Roman Tahoma Wingdings Arial Arial Unicode MS Symbol Times Blends Microsoft Equation 30 Microsoft Word Picture Probability Distributions Random Variable Random variables can be discrete or continuous Probability functions Discrete example.
In real life we always encounter situations where we have to choose the best option to arrive with the right decision. Another special case of gamma probability distribution that is useful in statistical inference problems is the chi-square distribution. Purpose of use To decide the composition of a charity club membership working party comprising experienced members other members so that the probability that at least one or more experienced members would be included.
Calculates the probability mass function and lower and upper cumulative distribution functions of the hypergeometric distribution. Method 1 of 3. In probability theory and statistics the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments each asking a yesno question and each with its own Boolean-valued outcome.
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur or how likely it is that a proposition is true. AnyDice is an advanced dice probability calculator available online. The normal distribution is the most important in statistics.
Finding the Probability of a Single Random Event. And our normal distribution is going to have a mean its going to have a mean right over here of so this is the mean of our sampling distribution so this is going to be equal to the same thing as our population proportion 015 and we also know that our standard deviation here is going to be approximately equal to 0028 and what we want to know is what is the approximate probability. When you have a set of data that you think might have a normal distribution ie.
Let n be a positive integer. This may be due to many reasons such as the stochastic nature of the domain or an exponential number of. Success with probability p or failure with probability q 1 pA single successfailure.
In this article well walk you through exactly how to use the probability formula step by step plus show you some examples of the probability formula in action. Poisson Distribution in Excel.

Understanding Probability Distributions Statistics By Jim

Understanding And Choosing The Right Probability Distributions With Examples By Kessie Zhang Towards Data Science

Understanding Probability Distributions Statistics By Jim
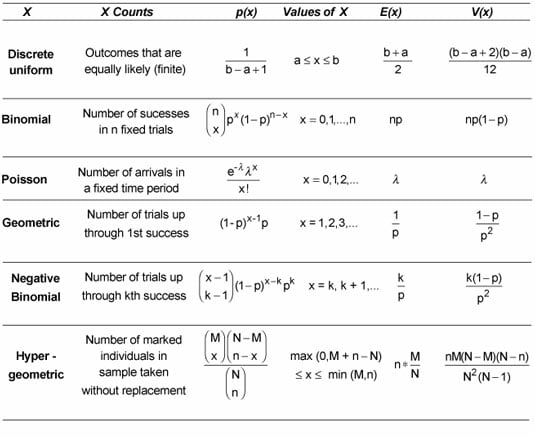
Probability For Dummies Cheat Sheet Dummies

Understanding And Choosing The Right Probability Distributions With Examples By Kessie Zhang Towards Data Science

Valid Discrete Probability Distribution Examples Video Khan Academy
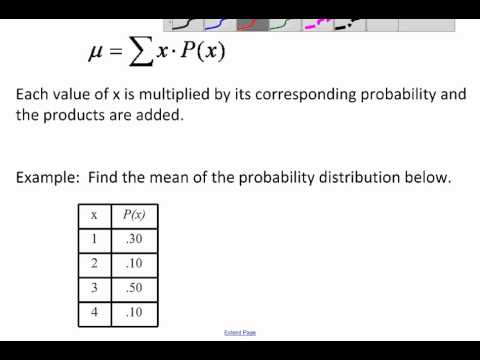
Mean Of A Probability Distribution Youtube
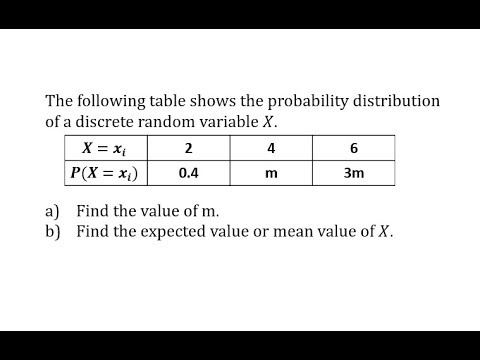
Find Probabilities And Expected Value Of A Discrete Probability Distribution Youtube

How To Find The Mean Of A Probability Distribution With Examples Statology
No comments for "How to Decide Which Probability Distribution to Use"
Post a Comment